The Connection Between Nutrition and Mental Health
The intricate relationship between what we eat and how we feel is a fascinating area of study, revealing that nutrition plays a significant role in mental health. As research continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly clear that our dietary choices can have profound effects on our emotional well-being.
Understanding the link between nutrition and mental health can empower individuals to make dietary choices that support not only physical health but also emotional stability. Nutritionist Amanda Geary highlights that, “A balanced diet is a key component of maintaining mental health and well-being.” This sentiment is echoed by numerous studies indicating that nutrient-rich foods can help in managing mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Exploring the Evidence
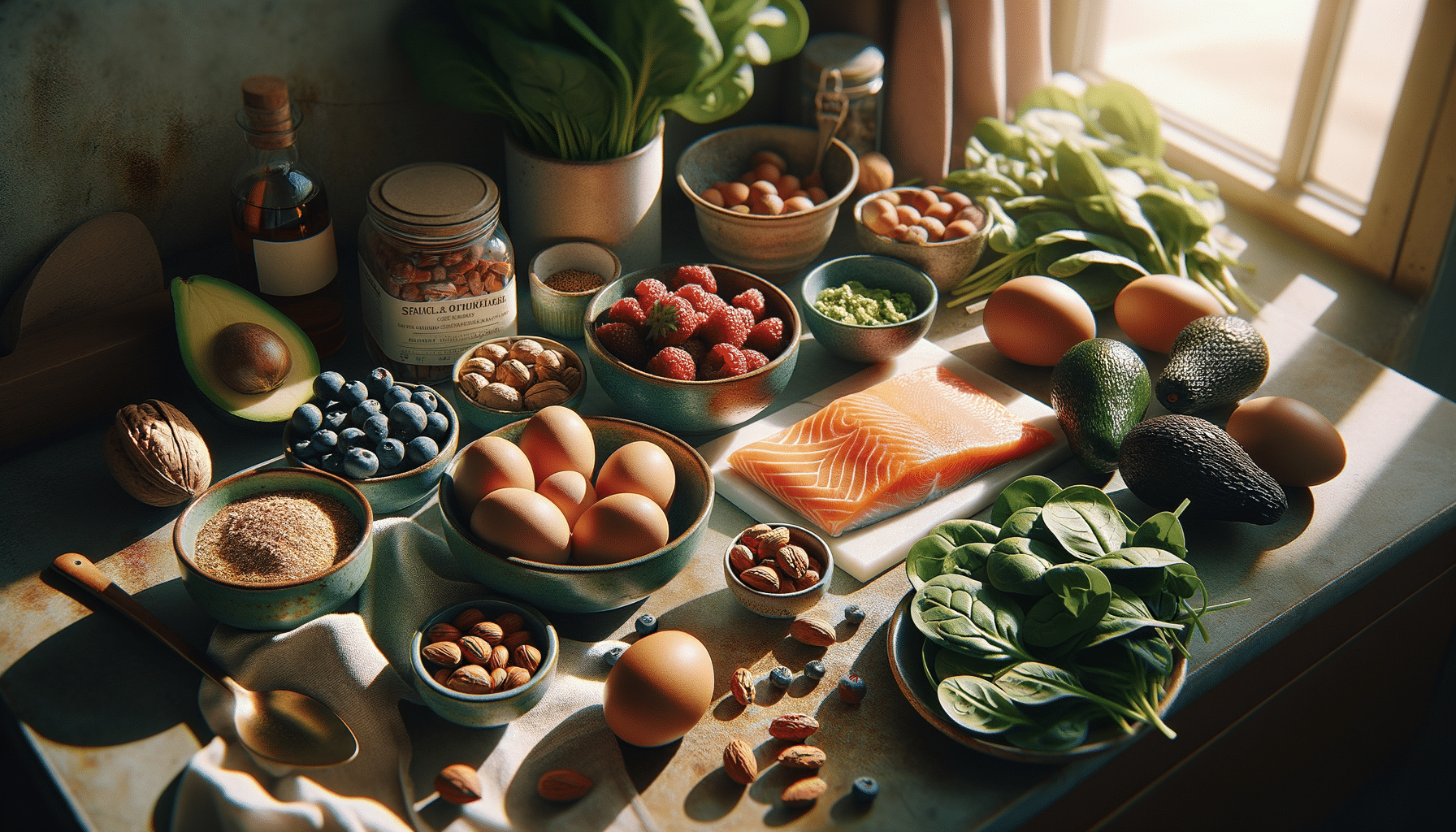
Research has shown that diets high in processed foods and low in nutrients are often associated with an increased risk of mental health disorders. A study conducted by the University of Melbourne found that individuals who consume diets rich in fruits, vegetables, fish, and whole grains tend to have lower rates of depression and anxiety. Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and mackerel, have been linked to improved mood and cognitive function.
Personal Stories
Consider the story of Mark, a 45-year-old who struggled with anxiety for years. Upon the advice of his healthcare provider, he incorporated more nutrient-dense foods into his diet, such as leafy greens and nuts. Within months, Mark noticed a significant improvement in his mood and energy levels. His experience underscores the potential benefits of dietary changes on mental health.
Actionable Tips
- Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into your meals to ensure a wide range of nutrients.
- Opt for whole grains over refined grains to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as flaxseeds and fish, in your diet.
- Stay hydrated, as dehydration can negatively impact mood and cognitive function.
Making Informed Choices
To better understand the nutritional content of common foods, refer to the table below:
| Food | Key Nutrients | Mental Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Spinach | Iron, Magnesium | Reduces fatigue, supports neurotransmitter function |
| Salmon | Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Improves mood, supports brain health |
| Nuts | Vitamin E, Healthy Fats | Protects brain cells, reduces oxidative stress |
| Whole Grains | Fiber, B Vitamins | Stabilizes mood, energy levels |
| Berries | Antioxidants, Vitamin C | Reduces inflammation, boosts brain function |
| Yogurt | Probiotics, Calcium | Improves gut health, which is linked to mood |
| Avocado | Healthy Fats, Potassium | Supports brain health, reduces stress |
| Flaxseeds | Omega-3s, Fiber | Improves mood, reduces inflammation |
FAQ
How does diet affect mental health?
Diet impacts mental health by influencing brain function and mood through nutrients that support neurotransmitter production and reduce inflammation.
What foods are good for mental health?
Foods rich in omega-3s, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, such as fish, berries, and leafy greens, are beneficial for mental health.
Can a poor diet lead to mental health issues?
Yes, diets high in processed foods and low in essential nutrients can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders.
In conclusion, the connection between nutrition and mental health is undeniable. By making informed dietary choices, you can positively impact your emotional well-being and overall quality of life. Start by incorporating more nutrient-rich foods into your daily routine and observe the potential changes in your mood and mental clarity. For further reading, consider exploring resources from reputable organizations such as the World Health Organization or the American Psychological Association.